STRIDE Overview: Difference between revisions
(Created page with '<span style="#color:#0067A5"> <font size="5"> Welcome to the STRIDE™ Test System Overview </font> </span> STRIDE has been uniquely designed for '' '''On-Target Expectation Te…') |
No edit summary |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<span style="#color:#0067A5"> <font size="5"> Welcome to the STRIDE™ | <span style="#color:#0067A5"> <font size="5"> Welcome to the STRIDE™ Wiki </font> </span> | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
STRIDE™ is a '''test infrastructure''' used by engineers to implement and execute tests for validating embedded software executing On-Target. STRIDE has been designed specifically for '''On-Target White-box Testing'''. | |||
STRIDE | The STRIDE system consists of: | ||
; A software ''Framework'' | |||
: enabling the creation of fully automated '''''Test Assets''''' used to verify the internal design of your software | |||
; A hosted ''Web Application - [[STRIDE_Overview#STRIDE_Test_Space | '''Test Space''']] | |||
: | : for storing and analyzing test results, thus providing on-demand availability of timely, accurate, and meaningful test results data | ||
STRIDE | ==STRIDE Framework == | ||
[[image:STRIDE 4.2 Framework-a.jpg |right|400px|border ]] | |||
The | ===Runtime=== | ||
The STRIDE Framework includes a [[Runtime_Reference | '''Runtime''']] software source package that supports connectivity with the host system. It is integrated with embedded application software to enable ''testability'' to be compiled into the software with minimal impact on performance or the size of the application. The software is agnostic to the RTOS, CPU, and transport. It can be configured to support multi-processes, multi-threads, user/kernel spaces, or a simpler single application process. Typically the runtime is configured as a background thread and only executes when running tests. It provides [[Runtime_Test_Services | '''services for testing''']] and [[Source_Instrumentation_Overview | '''source instrumentation''']]. | |||
=== Runner === | |||
The '' '''Framework''' '' also contains a lightweight [[Stride_Runner | '''Runner''']] application that is a host-based command-line utility for interactive and automated test execution. It also provides services for result publishing to our [[STRIDE_Test_Space | '''hosted web application''']]. | |||
<br> | |||
===Build Tools=== | |||
[[image:STRIDE 4.2 Framework-b.jpg |right|300px | border]] | |||
< | The [[STRIDE_Build_Tools | '''STRIDE Build Tools''']] are a set of command-line utilities that integrate with your target software build process. They preprocess standard C/C++ header files that contain STRIDE test declarations to auto-generate source code comprising a custom [[Intercept_Module | '''Intercept Module''']]. The intercept module code is then built with the Runtime to provide ''fixturing'' and ''harnessing'' test logic as part of your build image. | ||
'' | |||
==STRIDE Test Space== | |||
[[image:STRIDE 4.2 Test Space.jpg | 430px | right | border]] | |||
Once tests have been implemented, they are executed using the host-based [[STRIDE_Runner | '''Runner''']] application. Resulting '''test reports''' can be automatically uploaded to our '''web application''' - [[STRIDE_Test_Space | '''STRIDE Test Space''']]. This application allows both local and distributed team members to track and collaborate on results. | |||
Failure resolution is optimized by centralizing results and providing specific source information related to failures. ''Test Space'' also has built-in '''collaboration features''' in the form of email notification for new results and regression against a baseline as well as messaging. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
== STRIDE Testing Features == | |||
STRIDE supports three general [[Types_of_Testing_Supported_by_STRIDE | '''types of testing''']]: | |||
* Unit Testing, | |||
* API Testing, and | |||
* Integration Testing. | |||
STRIDE has been designed to deliver a broad spectrum of [[What_is_Unique_About_STRIDE#STRIDE_offers_testing_techniques_for_deeper_coverage | '''testing capabilities''']] that enable teams to '''''test earlier and more effectively'''''. Unique features such as [[What_is_Unique_About_STRIDE#Test_Macros | '''assertion macros''']], [[What_is_Unique_About_STRIDE#Fixturing | '''fixturing''']], and [[What_is_Unique_About_STRIDE#Test_Doubles | '''function doubling''']] facilitate deeper test coverage of your software components. STRIDE also provides [[What_is_Unique_About_STRIDE#Expectations |'''Expectations''']] as an added validation technique. Expectation testing is unique in that it ''does not'' focus on calling functions and validating return values. The technique rather validates the expected sequencing of the software, along with state data, executing under normal operating conditions. | |||
Tests can be implemented in both [[What_is_Unique_About_STRIDE#C.2FC.2B.2B | '''native code''']] on the target and [[What_is_Unique_About_STRIDE#Script | '''script''']] on the host. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<hr/> | |||
<font size="3"> | |||
'''For more details refer to the following:''' | |||
<hr/> | |||
* [[ | * '''[[What is Unique About STRIDE | What is Unique About STRIDE]]''' | ||
* [[ | * '''[[Types of Testing Supported by STRIDE | Types of Testing Supported]]''' | ||
* [[ | * '''[[Frequently Asked Questions About STRIDE | Frequently Asked Questions]]''' | ||
</font> | |||
<hr/> | |||
For a '''PDF version''' of this article please click [[Media:STRIDE_4.2_Datasheet.pdf | '''HERE''']] | |||
For an '''overview screencast''' of STRIDE please click [[STRIDE_Overview_Video | '''HERE''']] | |||
<hr/> | |||
[[Category: Overview]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:45, 23 November 2010
Welcome to the STRIDE™ Wiki
STRIDE™ is a test infrastructure used by engineers to implement and execute tests for validating embedded software executing On-Target. STRIDE has been designed specifically for On-Target White-box Testing.
The STRIDE system consists of:
- A software Framework
- enabling the creation of fully automated Test Assets used to verify the internal design of your software
- A hosted Web Application - Test Space
- for storing and analyzing test results, thus providing on-demand availability of timely, accurate, and meaningful test results data
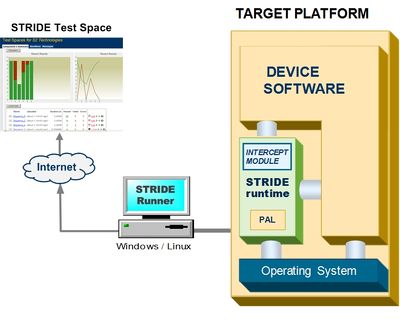
STRIDE Framework
Runtime
The STRIDE Framework includes a Runtime software source package that supports connectivity with the host system. It is integrated with embedded application software to enable testability to be compiled into the software with minimal impact on performance or the size of the application. The software is agnostic to the RTOS, CPU, and transport. It can be configured to support multi-processes, multi-threads, user/kernel spaces, or a simpler single application process. Typically the runtime is configured as a background thread and only executes when running tests. It provides services for testing and source instrumentation.
Runner
The Framework also contains a lightweight Runner application that is a host-based command-line utility for interactive and automated test execution. It also provides services for result publishing to our hosted web application.
Build Tools
The STRIDE Build Tools are a set of command-line utilities that integrate with your target software build process. They preprocess standard C/C++ header files that contain STRIDE test declarations to auto-generate source code comprising a custom Intercept Module. The intercept module code is then built with the Runtime to provide fixturing and harnessing test logic as part of your build image.
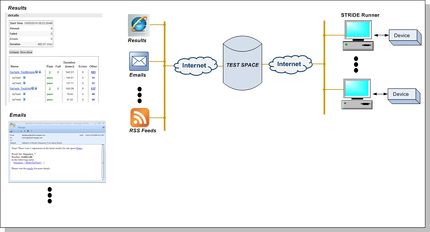
STRIDE Test Space
Once tests have been implemented, they are executed using the host-based Runner application. Resulting test reports can be automatically uploaded to our web application - STRIDE Test Space. This application allows both local and distributed team members to track and collaborate on results.
Failure resolution is optimized by centralizing results and providing specific source information related to failures. Test Space also has built-in collaboration features in the form of email notification for new results and regression against a baseline as well as messaging.
STRIDE Testing Features
STRIDE supports three general types of testing:
- Unit Testing,
- API Testing, and
- Integration Testing.
STRIDE has been designed to deliver a broad spectrum of testing capabilities that enable teams to test earlier and more effectively. Unique features such as assertion macros, fixturing, and function doubling facilitate deeper test coverage of your software components. STRIDE also provides Expectations as an added validation technique. Expectation testing is unique in that it does not focus on calling functions and validating return values. The technique rather validates the expected sequencing of the software, along with state data, executing under normal operating conditions.
Tests can be implemented in both native code on the target and script on the host.
For more details refer to the following:
For a PDF version of this article please click HERE
For an overview screencast of STRIDE please click HERE