Running Tests: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
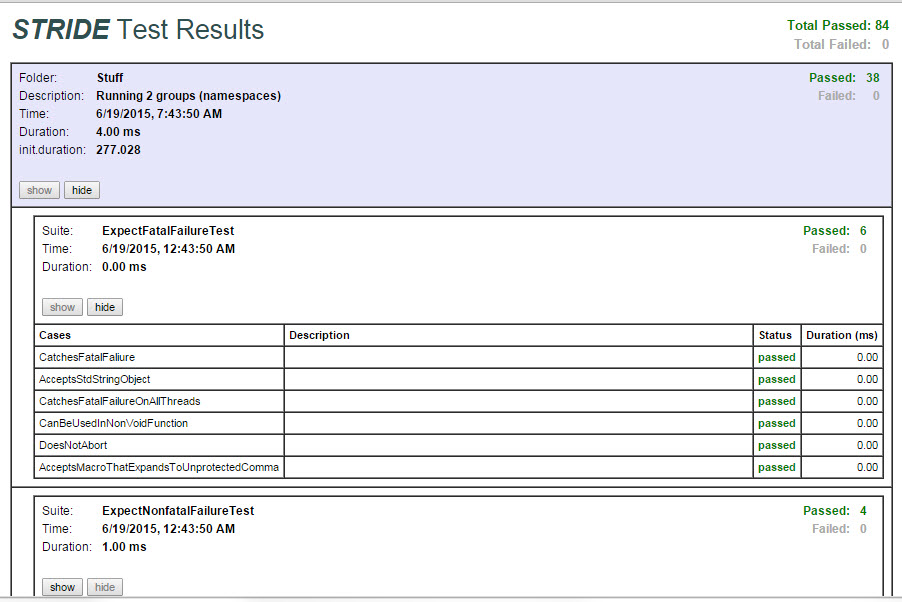
Stride executes tests using a runner controlled by a host computer that is physically connected to the target via a configurable communication channel (TCP/IP or serial port). The application software is required to be running, including the Stride runtime, to connect to the Stride Runner. | Stride executes tests using a runner controlled by a host computer that is physically connected to the target via a configurable communication channel (TCP/IP or serial port). The application software is required to be running, including the Stride runtime, to connect to the Stride Runner. | ||
''' | '''Block diagram''' | ||
[[Image:Running_Tests.jpg|500px|Connection Block Diagram]] | |||
Revision as of 20:55, 1 July 2015
Stride executes tests using a runner controlled by a host computer that is physically connected to the target via a configurable communication channel (TCP/IP or serial port). The application software is required to be running, including the Stride runtime, to connect to the Stride Runner.
Block diagram
Invoking the Runner (aka stride) from a console
stride --database="%STRIDE_DIR%\SDK\Windows\out\TestApp.sidb" --device=TCP:localhost:8000 --run="*"
or for Linux/FreeBSD
stride --database="$STRIDE_DIR%/SDK/Posix/out/TestApp.sidb" --device=TCP:localhost:8000 --run="*"
Option files can be helpful (i.e. my.opt)
--database "%STRIDE_DIR%\SDK\Windows\out\TestApp.sidb" --device TCP:localhost:8000
stride --options_file my.opt --run "*"
Reviewing your Results