STRIDE Runtime
Overview
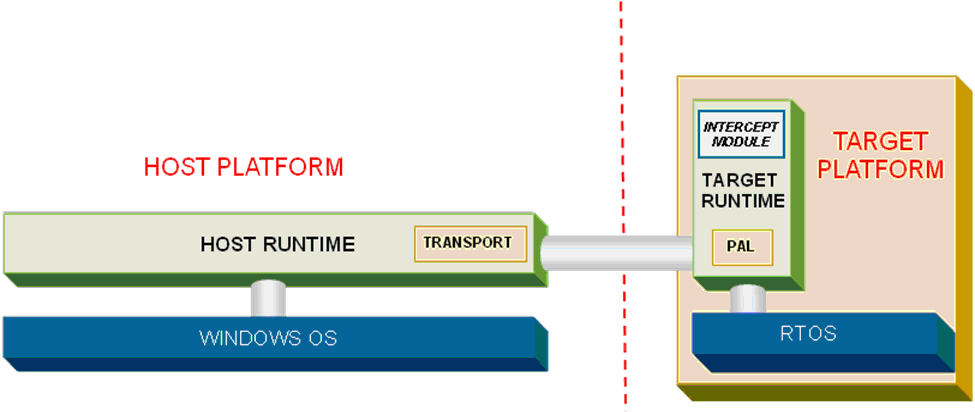
The STRIDE Runtime routes messages both within and between platform boundaries and manages the conversion of interface data as it crosses from one platform to another. This "transparent messaging" model means that your test cases can be located on one platform (e.g., as a script running off-target) and your code on another (on-target).
The Runtime Developer's Guide
Click [here] to view the STRIDE Runtime Developer's Guide PDF document.
The Platform Abstraction Layer Specification
The Platform Abstraction Layer, or PAL, defines the set of OS functionality required by the platform to support the STRIDE Runtime. The “pal.h” header file provided with the STRIDE installation defines the PAL functionality. The PAL also defines functionality required by the STRIDE Runtime to transmit and receive packets of data (called I-blocks) using the platform’s transport mechanism. These PAL routines enable the STRIDE Runtime to be installed on diverse environments without changing its internal design.
Click [here] to view the STRIDE Platform Abstraction Layer (PAL) Specification PDF document.
The Host Transport Specification
Click [here] to view the STRIDE Host Runtime Transport Specification PDF document.
The Transport Server Object Model
Follow this link for a discussion of the Transport Server Object Model.